The Countdown QuickPerm Algorithm (Head):
(Formally Example_01_Alpha)
QuickPerm - Head Permutations Using a Linear Array Without Recursion (Alpha)
// NOTICE: Copyright 1991-2008, Phillip Paul Fuchs#define N 12// number of elements to permute. Let N > 2void QuickPerm(void) { unsigned int a[N], p[N+1]; register unsigned int i, j, tmp;// Upper Index i; Lower Index jfor(i = 0; i < N; i++)// initialize arrays; a[N] can be any type{ a[i] = i + 'A';// a[i] value is not revealed and can be arbitraryp[i] = i; } p[N] = N;// p[N] > 0 controls iteration and the index boundary for i //display(a, 0, 0); // remove comment to display array a[]i = 1;// setup first swap points to be 1 and 0 respectively (i & j)while(i < N) { p[i]--;// decrease index "weight" for i by onej = i % 2 * p[i];// IF i is odd then j = p[i] otherwise j = 0tmp = a[j];// swap(a[j], a[i])a[j] = a[i]; a[i] = tmp;//display(a, j, i); // remove comment to display target array a[]i = 1;// reset index i to 1 (assumed)while (!p[i])// while (p[i] == 0){ p[i] = i;// reset p[i] zero valuei++;// set new index value for i (increase by one)}// while(!p[i])}// while(i < N)}// QuickPerm()
QuickPerm Function to Display Permutations (Optional)
// NOTICE: Copyright 1991-2008, Phillip Paul Fuchsvoid display(unsigned int *a, unsigned int j, unsigned int i) { for(unsigned int x = 0; x < N; x++) printf("%c ",a[x]); printf(" swapped(%d, %d)\n", j, i); getch();// press any key to continue...}// display()
Fundamental Analysis of the QuickPerm Algorithm Above {Switch to Numbers}
Number of Objects
to Permute (N)a[N] Display of
Initial Sequencea[N] Display of
Final SequenceTotal Number of Unique
Combinations Produced (N!)3 A B C C B A {Output} 2 * 3 = 6 4 A B C D D A B C {Output} 6 * 4 = 24 5 A B C D E E B C D A {Output} 24 * 5 = 120 6 A B C D E F F C D A B E 120 * 6 = 720 7 A B C D E F G G B C D E F A 720 * 7 = 5040 8 A B C D E F G H H C D E F A B G 5040 * 8 = 40320 9 A B C D E F G H I I B C D E F G H A 40320 * 9 = 362880 if N is even A B C . . . (N - 1) N N C D . . . (N - 2) A B (N - 1) (N - 1)! * N = N! if N is odd A B C . . . (N - 1) N N B C . . . (N - 1) A (N - 1)! * N = N!
A Permutation Ruler:
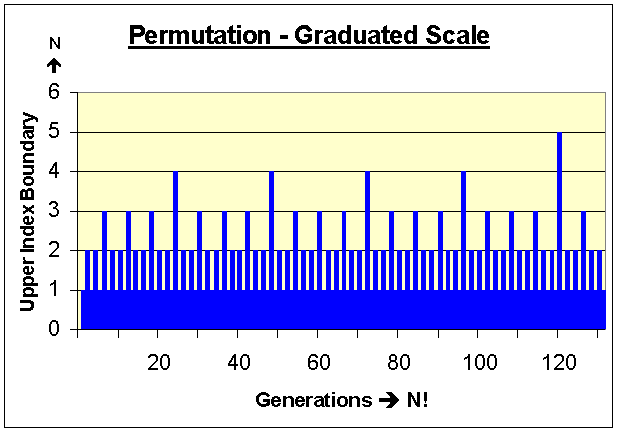
(Click here to enlarge graph.)
Next is tail permutations represented in EXAMPLE 02.

