| Number of Objects to Permute (N) |
a[N] Display of Initial Sequence |
a[N] Display of Final Sequence |
Total Number of Unique Combinations Produced (N!) |
| 3 | A B C | C B A {Output} | 2 * 3 = 6 |
| 4 | A B C D | D A B C {Output} | 6 * 4 = 24 |
| 5 | A B C D E | E B C D A {Output} | 24 * 5 = 120 |
| 6 | A B C D E F | F C D A B E | 120 * 6 = 720 |
| 7 | A B C D E F G | G B C D E F A | 720 * 7 = 5040 |
| 8 | A B C D E F G H | H C D E F A B G | 5040 * 8 = 40320 |
| 9 | A B C D E F G H I | I B C D E F G H A | 40320 * 9 = 362880 |
| if N is even | A B C . . . (N - 1) N | N C D . . . (N - 2) A B (N - 1) | (N - 1)! * N = N! |
| if N is odd | A B C . . . (N - 1) N | N B C . . . (N - 1) A | (N - 1)! * N = N! |
A Permutation Ruler:
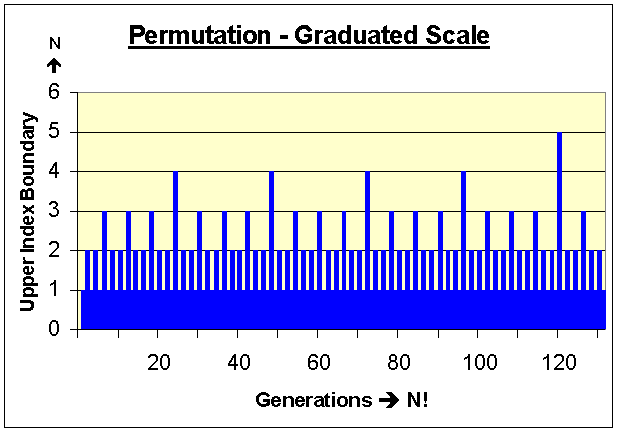
 (Click here to enlarge graph.)
(Click here to enlarge graph.)Next is tail permutations represented in EXAMPLE 02.